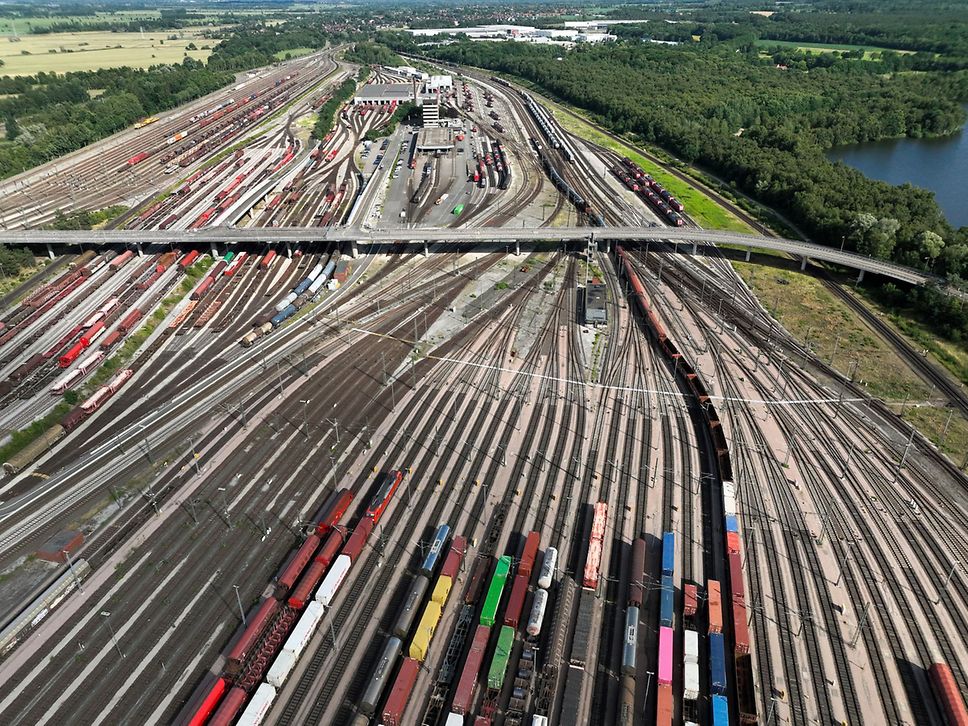
Train classification is at the heart of DB Cargo's logistics processes and a central component of single freight car transport. It includes all measures for the composition and breakdown of freight trains and ensures that goods reach their destination efficiently and punctually. Here we provide an insight into the complex processes and strategies behind train classification.
What exactly does train classification mean?
Train classification is the process of organizing and assembling freight cars into a train ready for transport. This process begins with the arrival of the individual freight cars in a classification yard and ends with the departure of a fully assembled freight train. Each wagon carries different freight goods that need to be transported to different destinations. The art of train classification lies in combining these wagons in such a way that they optimally reach their destinations, minimizing transport times while making maximum use of capacities.
The processes of train classification
Train classification begins long before the freight cars arrive at the classification yard. It requires careful planning and coordination to ensure that all wagons arrive on time and in the right order. These are the main steps at a glance:
• Receiving and sorting: On arrival, the freight cars are first registered and dispatched according to their destinations. This usually takes place on special entry tracks.
• Foreman shunting and grouping: The freight cars are then regrouped on classification tracks. This is done with the help of switching locomotives, which assemble the wagons into new convoys, or with the help of a hump, where the wagons roll into the new sorting sidings. Care is taken to ensure that wagons with similar destinations are brought together.
• Technical inspection: Every convoy undergoes a technical inspection. This inspection ensures that all wagons are in perfect condition and meet safety standards.
• Preparation for departure: Before the train leaves the station, a final check is carried out and the locomotive is coupled. The train driver receives all the necessary documents and information for the journey.
Strategies to increase efficiency
Efficiency in train classification is a decisive factor in how much freight is transported by rail. DB Cargo is therefore working on making the process even more effective. These measures, among others, play a role in this:
• Automation and digitalization: Modern classification yards rely on automatic coupling systems and digital shunting assistants that speed up train composition and reduce errors.
• Just-in-time strategies: Precise scheduling and real-time communication ensure that trolleys arrive exactly when they are needed. This minimizes waiting times and increases efficiency.
• Customised solutions : Close cooperation with customers and partners enables flexible and demand-oriented train classification. Customized solutions allow individual requirements to be better met.
• Environmentally friendly logistics: By using energy-efficient and modern locomotives and optimizing train length and load, DB Cargo is helping to reduce its environmental footprint and offer more sustainable transport solutions.
The importance for the logistics chain
Efficient train classification is a central building block in the logistics of rail freight transport. It ensures that goods reach their destination punctually and reliably, thus making a significant contribution to customer satisfaction. It also makes it possible to make optimum use of resources and reduce costs.